In the quest for more efficient, sustainable, and technologically advanced aerospace designs, the search for innovative materials has taken center stage. The aerospace industry demands materials that can withstand extreme conditions, from the intense pressures and temperatures of launches to the frigid vacuum of space. As such, engineers and scientists are continuously developing cutting-edge materials that achieve a delicate balance between reducing weight and maintaining strength—a necessity for performance and economic viability.
One of the most promising areas in this field is the development of composite materials. These materials combine two or more constituents, often yielding extraordinary properties that single materials cannot achieve alone. The most common composite materials in aerospace are carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRPs), which have revolutionized aircraft and spacecraft design due to their high strength-to-weight ratios. Companies like Boeing and Airbus have already integrated CFRPs extensively into their airframes, leading to lighter aircraft that require less fuel and can transport more payloads efficiently.
Advancements in nanotechnology are also enabling the development of novel materials with previously impossible characteristics. Carbon nanotubes and graphene, materials composed of carbon atoms in a single layer that are arranged in a hexagonal lattice, exhibit remarkable strength and conductivity. Incorporating these materials into composites could drastically reduce the weight of aerospace components while enhancing their mechanical properties. These enhancements not only improve performance but also extend the lifespan of parts by making them more resistant to wear and environmental factors.
Another exciting innovation involves metallic foams. These materials are made by introducing gas bubbles into a metal matrix, resulting in a highly porous structure. Metallic foams offer an impressive strength-to-weight ratio and excellent energy absorption properties, making them ideal for crash-resistant structures and lightweight load-bearing applications. When used in conjunction with other materials, metallic foams can contribute to the development of multifunctional components that optimize weight and enhance safety.
The push towards sustainability is also influencing material research. Traditional metal alloys and composites often involve energy-intensive manufacturing processes and can be difficult to recycle. Researchers are now focusing on developing bio-composites derived from natural fibers and resins. These materials offer comparable mechanical properties to traditional composites but with a significantly lower environmental footprint. Additionally, efforts to improve the recyclability of high-tech composite materials are underway, aiming to create a circular lifecycle for components used in aerospace.
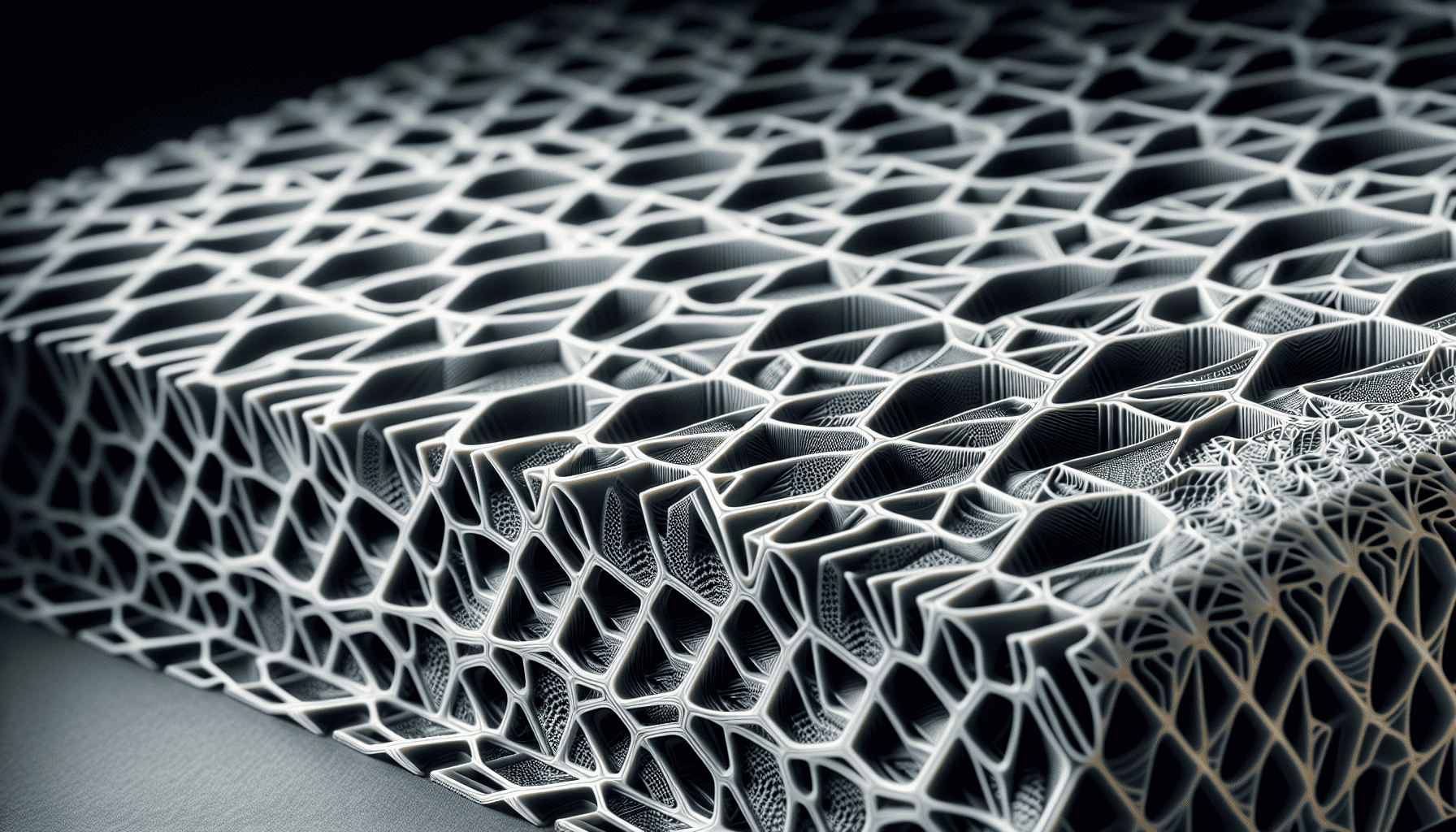
3D printing is another technological frontier that holds the promise of revolutionizing aerospace materials. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex geometries that are not possible with traditional manufacturing techniques, facilitating the reduction of weight without compromising structural integrity. Innovations in 3D printing materials, such as high-temperature thermoplastics and metal alloys, are expanding the possibilities for fabricating aerospace parts that meet the industry’s rigorous demands.
In conclusion, the continual advancement and innovation in aerospace materials are fueled by the unwavering pursuit of improved performance and sustainability. Whether it's through the integration of nanomaterials, the use of bio-composites, or the exploration of additive manufacturing techniques, these cutting-edge materials play a crucial role in shaping the future of aerospace technology. As engineers and scientists push the boundaries, they are setting the stage for a new era of aerial and space exploration characterized by lighter, stronger, and greener vehicles.